Heavy Equipment Shipping Statistics 2025–2026 (Costs, Trends & Industry Data)


Heavy equipment shipping is a specialized sector of logistics, responsible for moving oversized machinery for construction, mining, agriculture, and energy projects. With infrastructure spending rising worldwide, this industry continues to expand in both the U.S. and global markets. Below is a roundup of the latest statistics on costs, shipping methods, challenges, and future trends for 2025–2026.
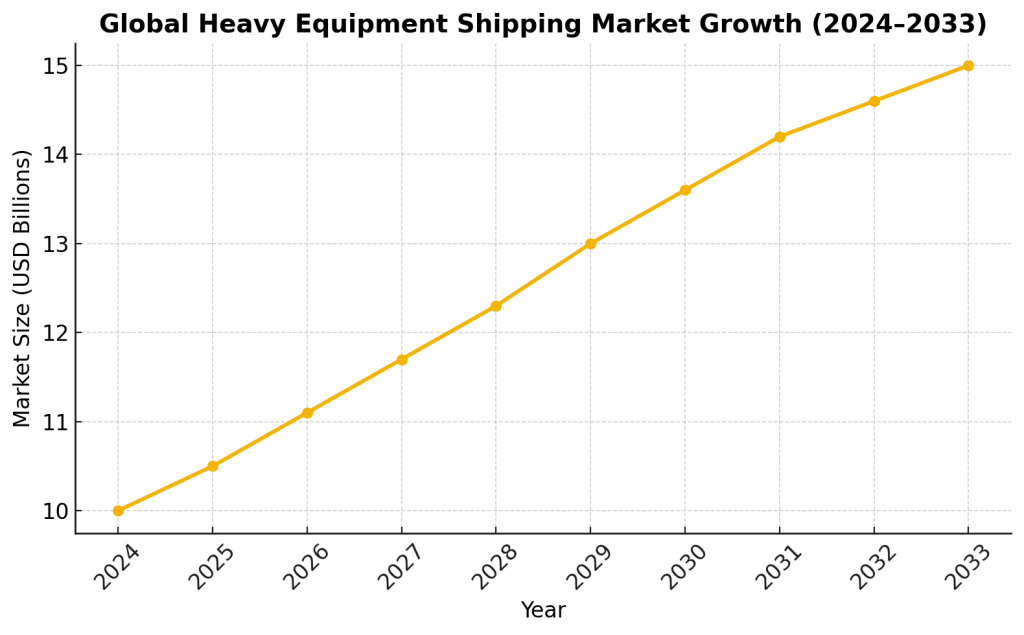
Heavy Equipment Shipping Market Size & Growth
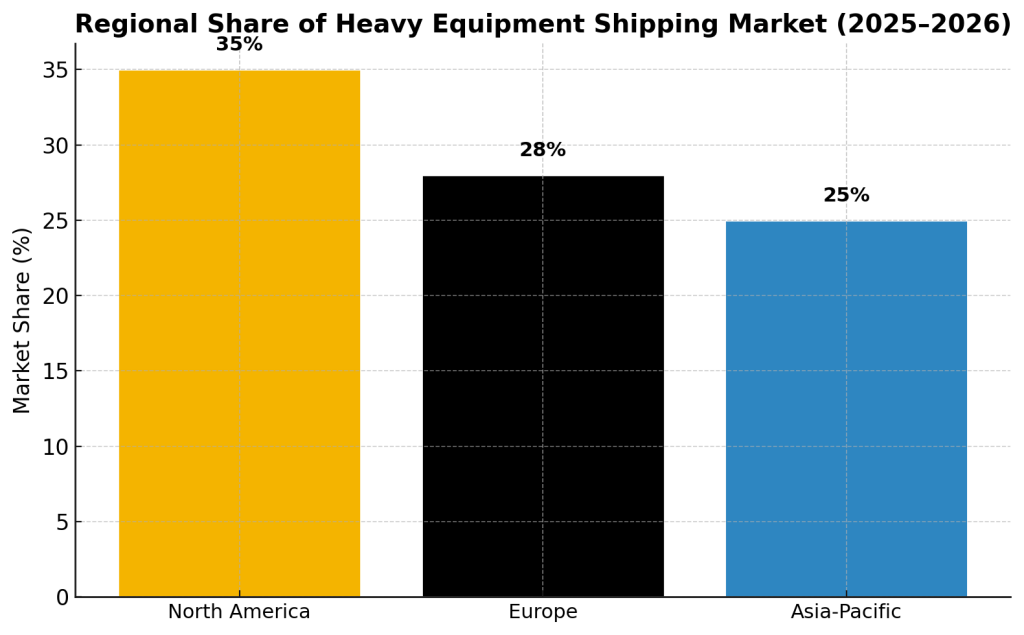
The heavy equipment shipping industry is expanding steadily, with North America holding the largest share and Asia-Pacific driving the fastest growth.
- The global heavy equipment transport services market is valued at $10 billion in 2024, projected to reach $15 billion by 2033 (Statista).
- North America holds 35% of global revenue (2023), followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (25%) (Market Research Future).
- U.S. heavy-haul freight services are growing at about 4.2% annually through 2025, supported by investments in infrastructure (U.S. Department of Transportation).
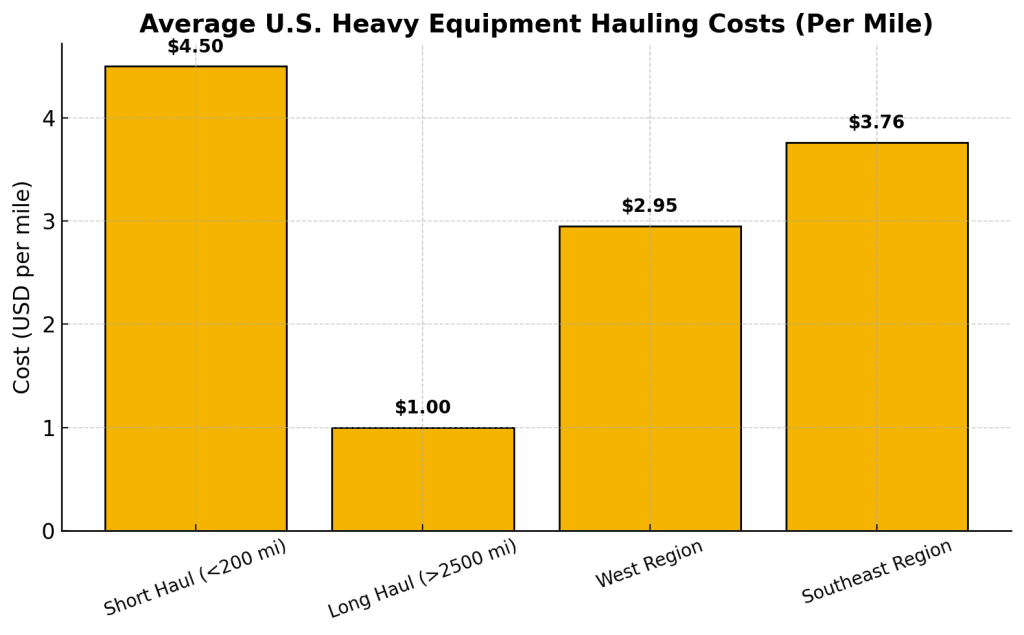
Average Costs of Shipping Heavy Equipment
Shipping costs depend on distance, size, and mode of transport. U.S. domestic shipments are priced per mile, while international moves add significant ocean freight costs.
- U.S. heavy equipment hauling costs average $3–$8 per mile, depending on route and load size.
- Long-haul shipments (>2,500 miles) can drop to ~$1 per mile (American Transportation Research Institute).
- Regional rates vary: $2.95/mile in Western states vs $3.76/mile in the Southeast (DAT Freight & Analytics).
- Ocean freight example: $1,876 for a 20-ft container from Shanghai to Los Angeles (Freightos).
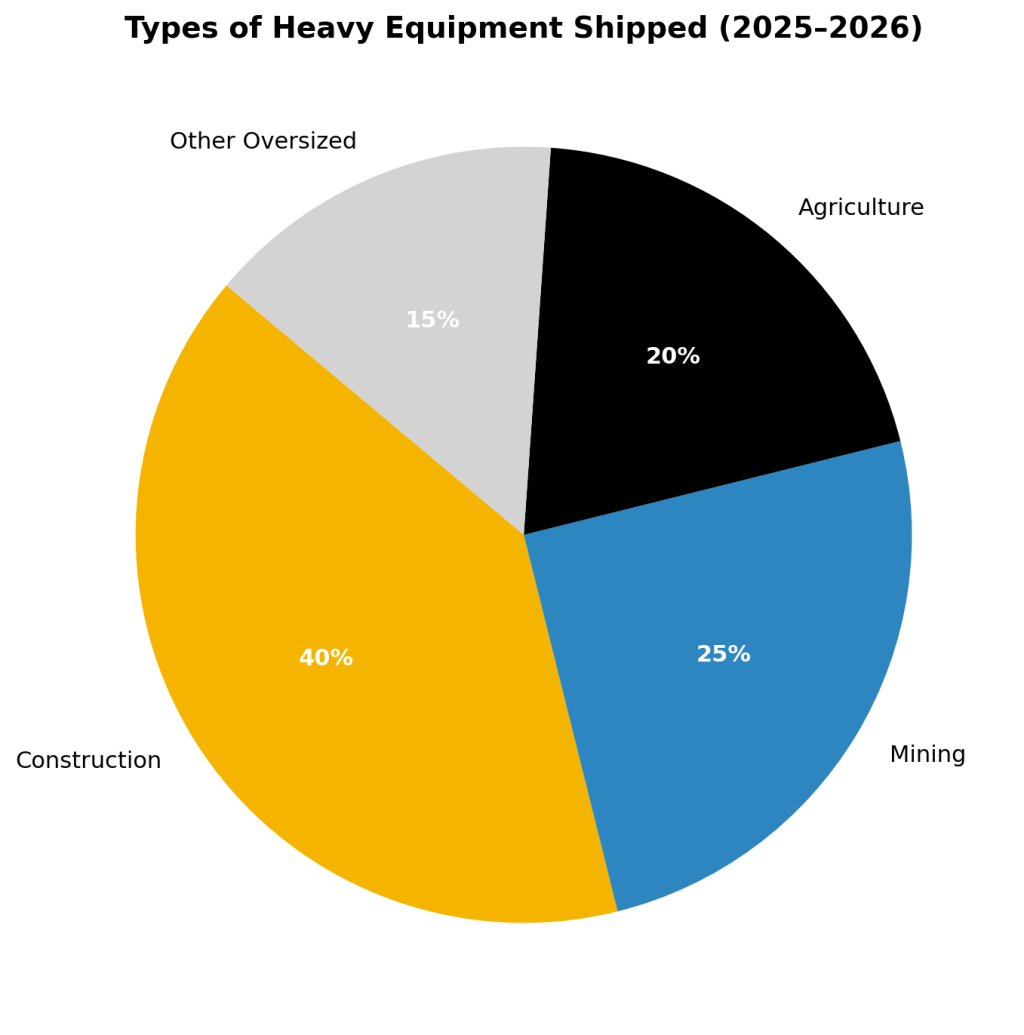
Types of Heavy Equipment Shipped
Construction machinery makes up the largest share of shipments, followed by mining and agriculture equipment.
- Construction machinery = ~40% of shipments (excavators, bulldozers, cranes) (AEM).
- Mining machinery = 25%, fastest-growing category (World Mining Equipment Outlook).
- Agricultural equipment = 20% (tractors, harvesters) (U.S. Census Bureau).
- Other oversized loads = 15% (industrial parts, turbines, military vehicles).
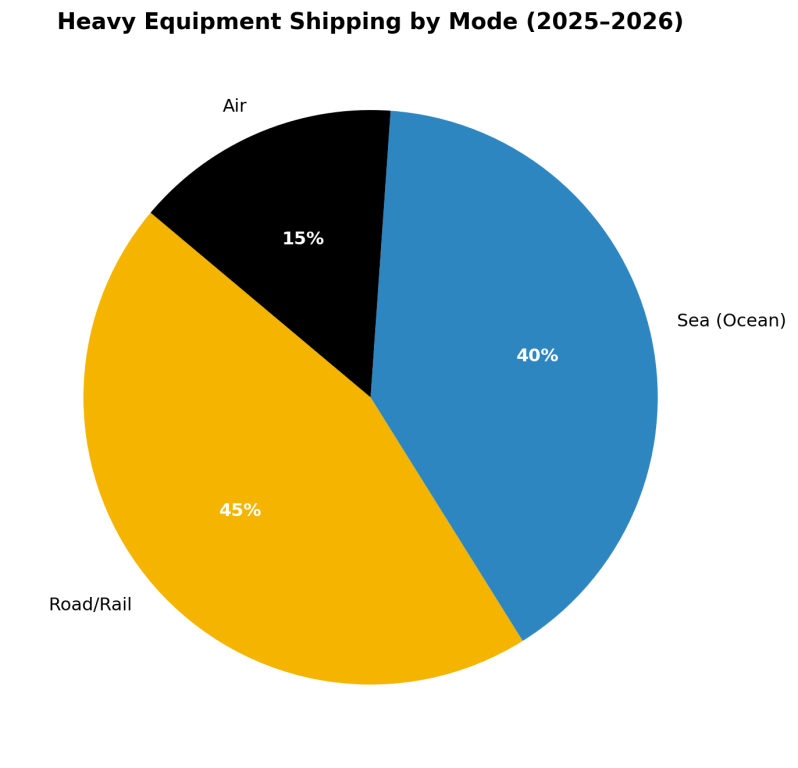
Shipping Methods: Road, Rail, Sea & Air
Most heavy equipment is transported overland by truck, but ocean shipping dominates international moves.
- Road/rail transport = 45% of global heavy equipment transport revenue (Market Research Future).
- Ocean shipping = 40%, vital for exports/imports (UNCTAD).
- Air freight = 15%, a niche but growing solution for urgent deliveries (IATA).
- Trucks handle 72.6% of all U.S. freight by weight (BTS).
Domestic vs. International Trends
Domestic U.S. shipping remains strong, but global trade in heavy equipment is rapidly increasing.
- North America = 35% of global heavy equipment shipping revenue (Market Research Future).
- Asia-Pacific = 25%, fastest growth region (World Bank).
- Europe = 28%, steady demand.
- Nearly 40% of shipments are ocean-based international moves (UNCTAD).
Delivery Times & Distances
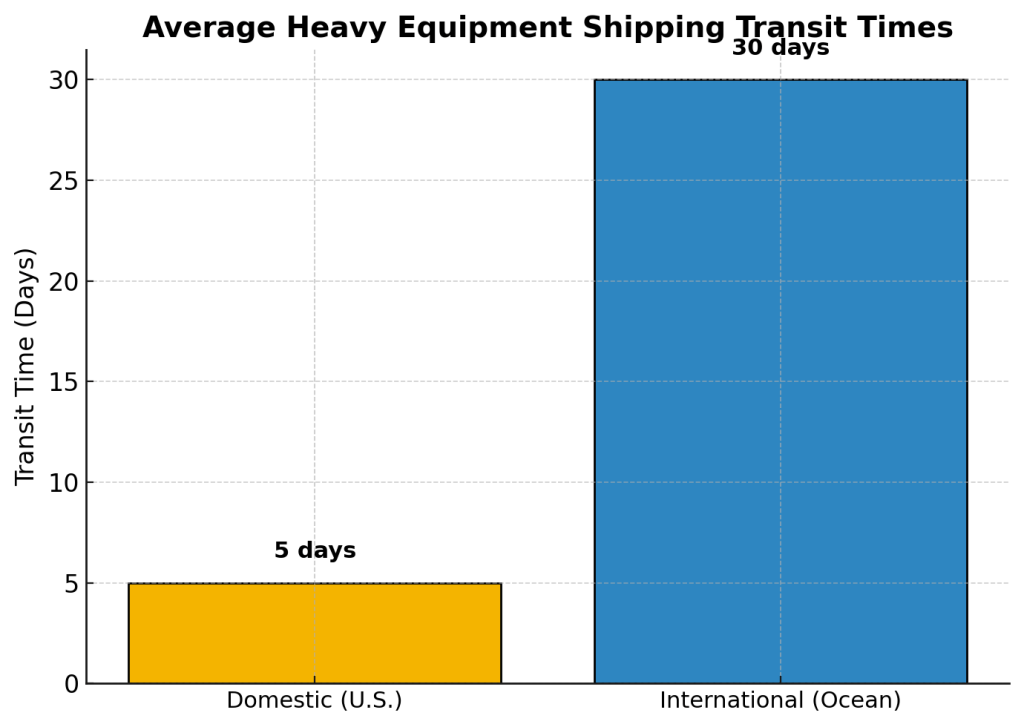
Heavy equipment shipping is time-intensive, especially for oversized loads and ocean freight.
- U.S. domestic shipments typically take 3–7 days (U.S. DOT).
- Example: New Orleans → New York (1,300 miles) = 4–6 days.
- Average U.S. freight haul = 500–600 miles, while heavy equipment often travels 1,000+ miles (FHWA).
- International ocean transit = 15–45 days port-to-port.
Challenges in Heavy Equipment Shipping
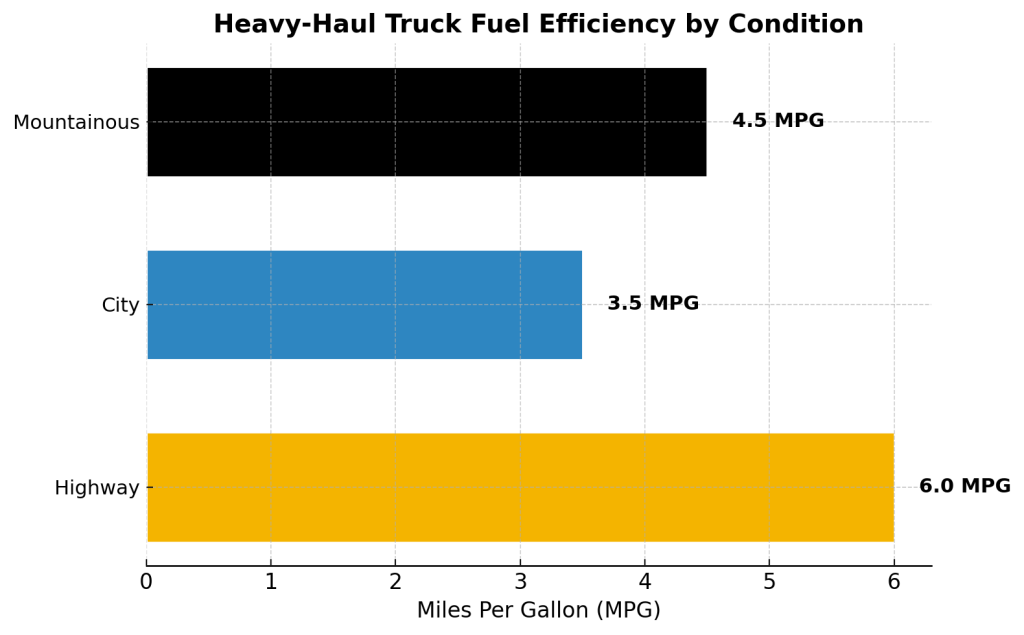
The industry faces regulatory, fuel, and labor-related challenges.
- All 50 states have unique oversize permit rules.
- Diesel price spikes (e.g. +25% in 2022) impacted shipping costs (U.S. Energy Information Administration).
- Heavy-haul trucks get just 3–6 MPG depending on load/terrain (Environmental Protection Agency).
- The trucking industry faces a 60,000+ driver shortage (AMT).
Future Trends 2026 & Beyond
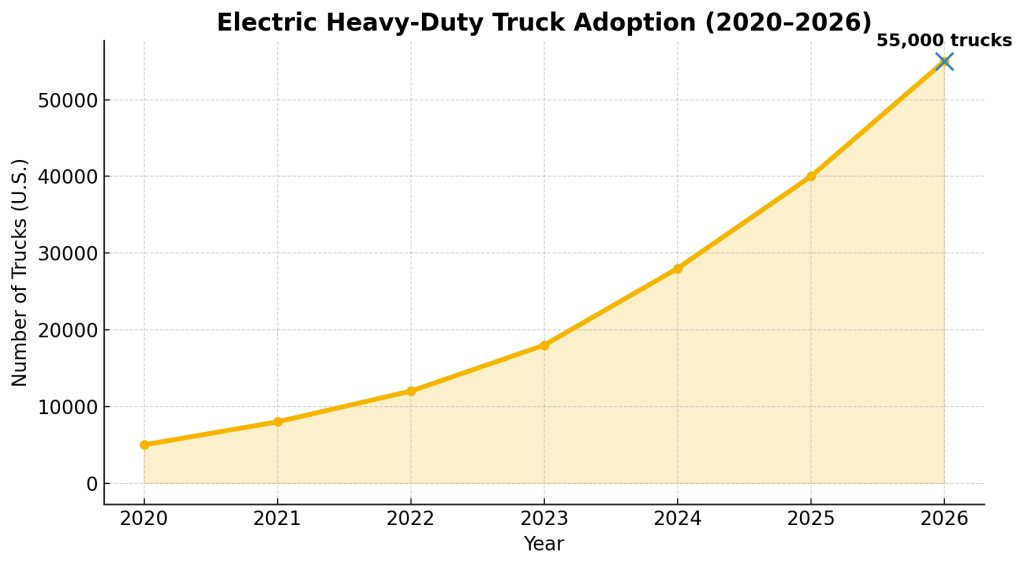
Technology and sustainability are shaping the future of heavy equipment logistics.
- Market forecast: 5%+ annual growth through the late 2020s.
- U.S. offering $40,000 EV truck tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act (White House Fact Sheet).
- About 30,000 electric trucks on U.S. roads by 2024 (<0.3% of fleet).
- Nearly 90% of logistics firms use GPS tracking, with AI adoption rising (FreightWaves).
Final Thoughts
Heavy equipment shipping plays a central role in infrastructure and industrial growth. With rising demand in the U.S. and abroad, costs and regulations remain challenges, but technology and sustainability will drive innovation. This dataset highlights the key numbers shaping the industry in 2025–2026.
If you’re planning a move for construction machinery, agricultural equipment, or oversized freight, A-1 Auto Transport provides reliable heavy equipment shipping services across the U.S. and internationally. Our specialized trailers, experienced drivers, and nationwide coverage ensure safe, on-time deliveries for even the largest loads.
Learn more about ourHeavy Equipment Shipping Services


 Share on Facebook
Share on Facebook Share on LinkedIn
Share on LinkedIn Share on Twitter
Share on Twitter Google
Google  Instagram
Instagram 



